Intelligent Automatic Differentiation
Kailai Xu, Dongzhuo Li, Eric Darve, and Jerry M. Harris. "Learning Hidden Dynamics using Intelligent Automatic Differentiation"
Dongzhuo Li, Kailai Xu, Jerry M. Harris, and Eric Darve. "Time-lapse Full Waveform Inversion for Subsurface Flow Problems with Intelligent Automatic Differentiation"
We treat physical simulations as a chain of multiple differentiable operators, such as discrete Laplacian evaluation, a Poisson solver and a single implicit time stepping for nonlinear PDEs. They are like building blocks that can be assembled to make simulation tools for new physical models.
Those operators are differentiable and integrated in a computational graph so that the gradients can be computed automatically and efficiently via analyzing the dependency in the graph. Independent operators are parallelized executed. With the gradients we can perform gradient-based PDE-constrained optimization for inverse problems.

This view of numerical simulation enables us to develope very sophisticated tools for inverse modeling: we decouple the individual operators and implement a forward/backward for each of them; they are consolidated using ADCME to create a computational graph. The computational dependency is then parsed and gradients are automatically computed based on the dependency. For example, in this work, we coupled multiphysics and obtain the gradients of the objective function with respect to the hidden dynamics parameters (i.e., permeability). This can be quite time-consuming and error-prone if we are going to derive the gradients by hand, implement and debug. With ADCME, we "chain" all the operators and the gradients are obtained automatically.
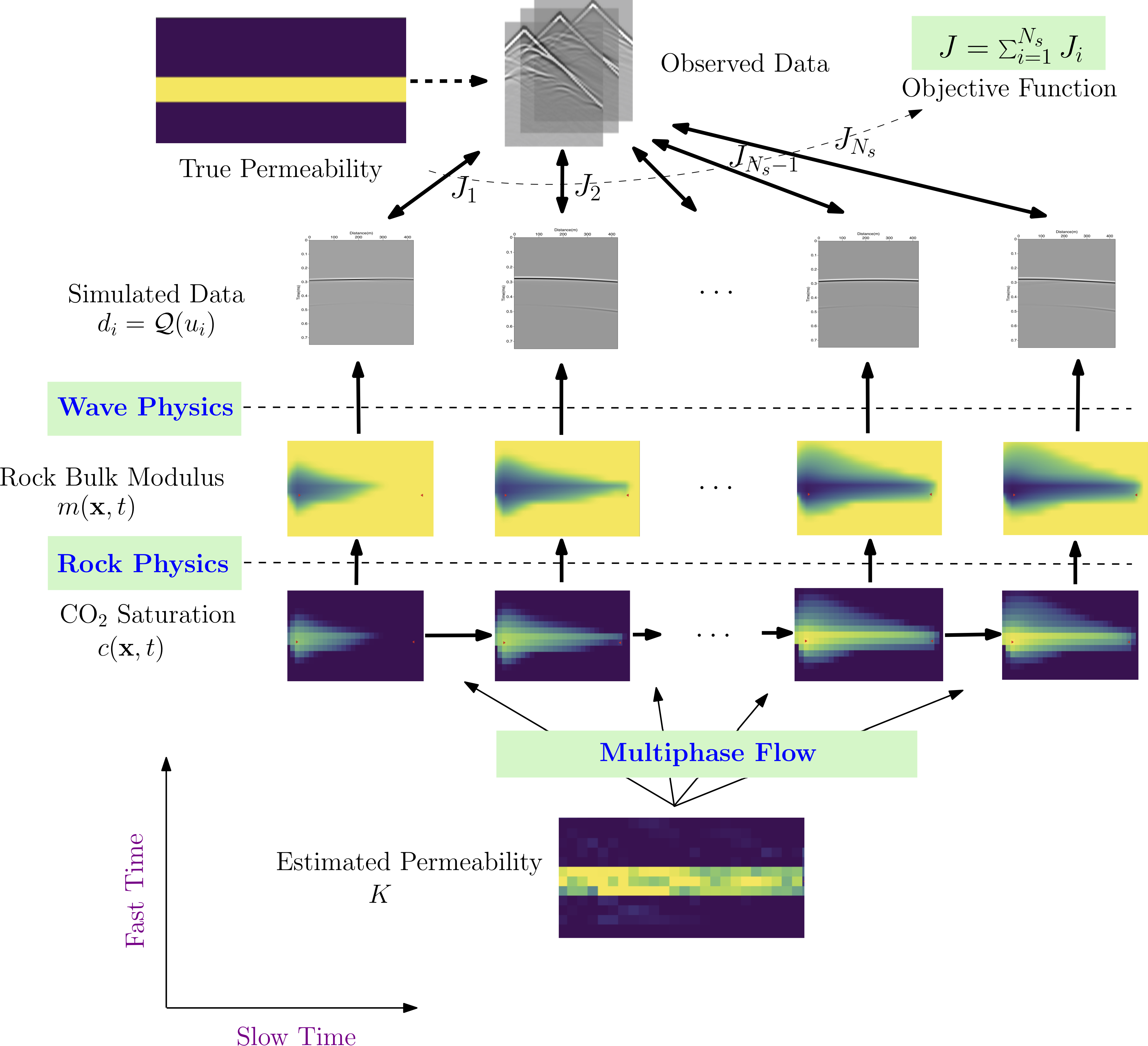
We call this technique intelligent automatic differentiation, since we can design our own operators for performance and those operators are submodules that can be flexibly replaced and reused. For more details, see FwiFlow.jl, a package focused on elastic full waveform inversion for subsurface flow problems.